Why Ball Bearings are used in Machines:
An Introduction to Ball Bearings
Ball bearings consist of a fixed housing casing and a rotating shaft. Together, they are the solution for getting the cogs turning in many industrial settings.
When you buy ball bearings in Singapore, and in other distribution locations around the world, it’s important to understand what exactly a ball bearing is, how it functions and which ball bearing types are suited to your mechanisms.
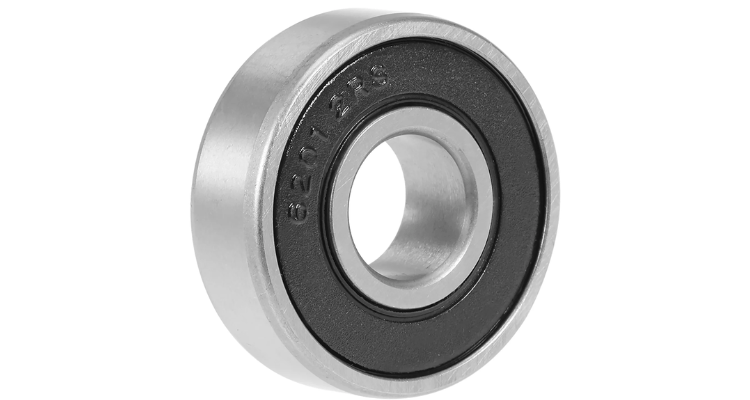
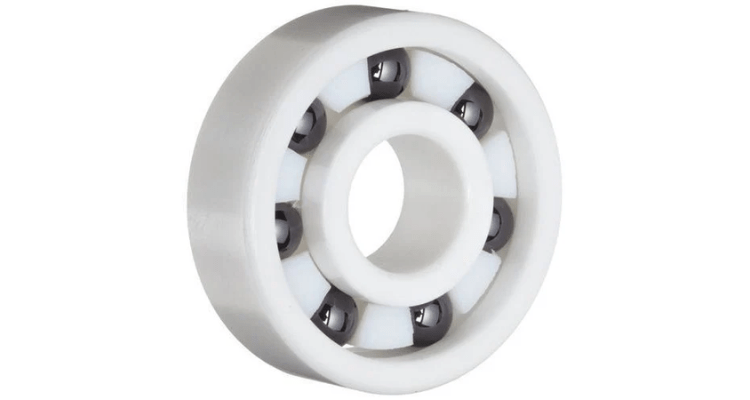
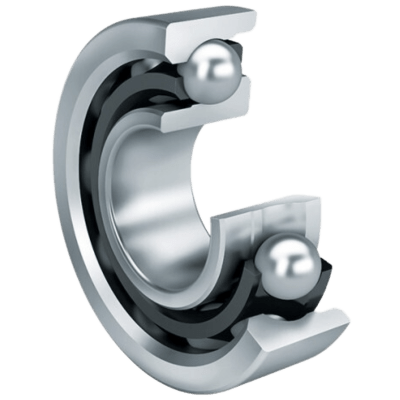
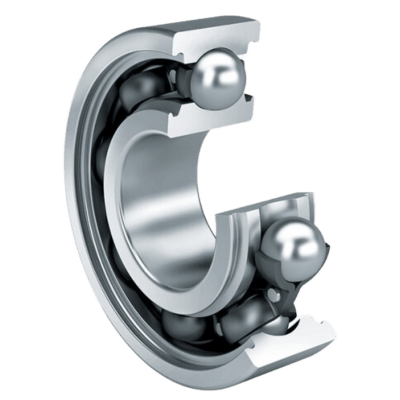
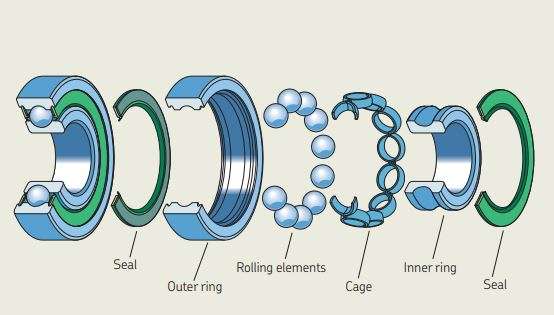
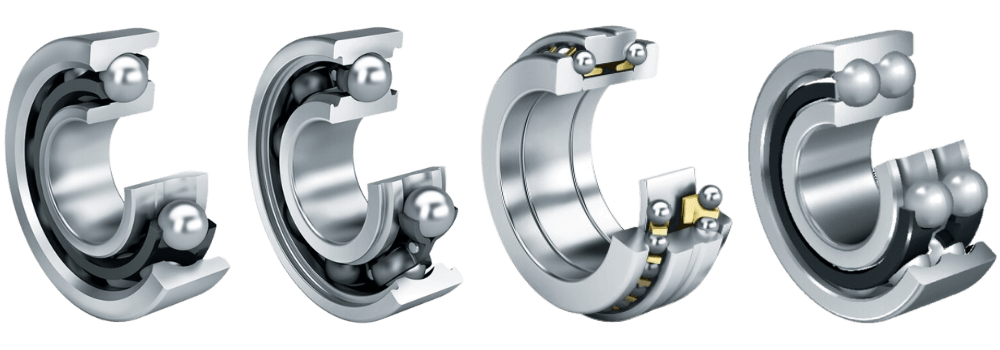
There are five main parts to the most common of the ball bearing family. They all work closely together in order to maintain frictionless stability and connection between two components.

1. The Steel Balls
Starting from the center of the ball bearing, steel balls hold the most crucial role in performing functionality. They represent the rolling element of the bearing.
2. The Cage
The cage holds the balls in a uniform ring keeping them at equidistant intervals within the bearing. The cage can be manufactured in a range of shapes and is developed using low-friction materials to allow the balls to continue rolling freely.
3. The Inner Ring
The inner ring (also referred to as the inner race) is a smaller piece on which the ball bearings sit on a radial axis. In most industry instances, it is the inner ring that spins as it is connected to the moving parts. The inner and outer races (see below) feature the same band width but varying ring diameters to allow for the insertion of the balls.
4. The Outer Ring
The outer ring (also referred to as the outer race) is the larger ring under which the balls maneuver on a radial axis. As the inner race typically features movement, it’s recognizable that the outer ring is the stagnant component. Both the outer ring and inner ring feature a groove of varying depths in order to allow the rolling elements glide without deviation.
5. The Shield
Finally, the shield is an optional component to the ball bearing. However, it is highly recommended that you buy ball bearings with the shield included. The reasoning behind this is due to the increased durability prospects; the shield is a cover hiding the rolling element. They can either be manufactured with metal to prevent the settling of dust or with plastic to increase water resistance. At the same time, these shields help retain oil and grease to reduce the need for maintenance as it is kept lubricated for the entire lifecycle.
In order to move correctly, bearings need a radial and axial clearance (internal clearance) of these five parts. This is to allow for thermal expansion when operating caused by remaining friction levels. This special grant prevents the bearing from tightening, wearing and seizing.
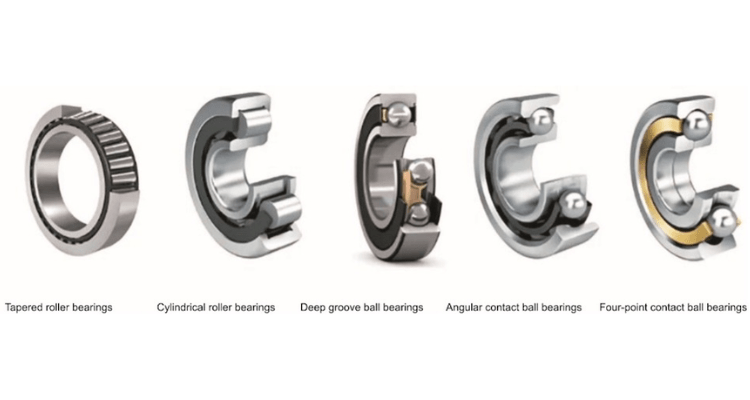
What are the Types of Bearings Available from a Bearing Supplier of Kolkata?
Bearings are not a one-size-fits all industrial component. So, when you go to the bearing supplier of Kolkata, you need to understand which bearing will fit your operation and machine.
-
Radial bearings are designed to withstand forces perpendicular to the access.
-
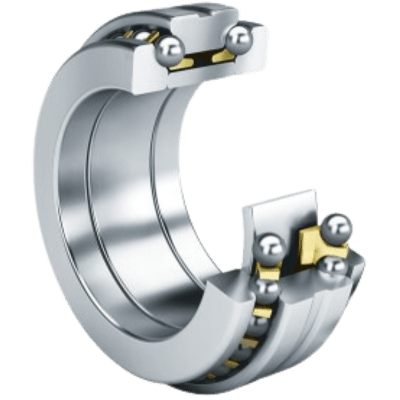
Axial bearings sandwich the balls between the races while withstanding axial forces.
-
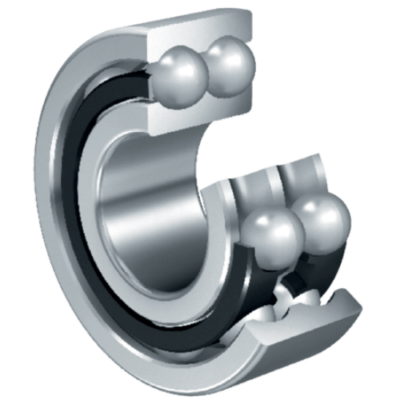
Angular contact bearings are designed to withstand both perpendicular and axial loads.
- Roller bearings are used to lower the friction rates between moving parts and carry a higher load capacity compared to ball bearings.
-
Linear bearings allow for movement in one direction such as back and forth.
-
Self-aligning bearings allow for the inclination of the axis through double-roll bearings while functioning.
- Mounted bearings are used to support rotating parts or separate rotating parts with stationary one.