Why Lubrication is Important for Bearings and Other Components
The key to reducing friction in transmission is precision, and bearing lubrication is the solution to ensure that the rolling component functions smoothly. There are numerous causes of bearing failure, such as incorrect mounting or overloading, and lubrication can also be a factor when the incorrect type is used, it is applied improperly, or the right preventative maintenance is not provided.
Why Lubrication in Bearings is Important
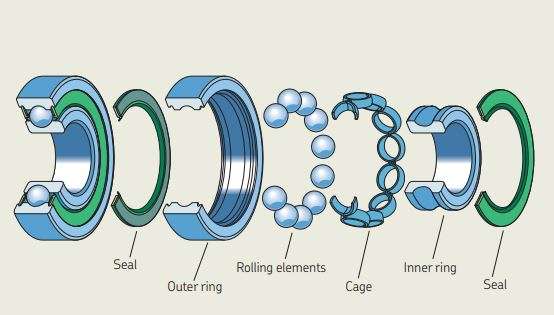
Apart from ensuring frictionless power transmission, lubrication also provides a protective barrier between the different components of the bearing, such as the rolling element, outer ring, inner ring, and shield, where necessary. This barrier offers various advantages that can increase the lifespan of the bearing, protect other machine components, and improve the overall production process.
Role of Lubrication in Bearings
- It prevents oxidization
- It minimizes corrosion
- It acts as a contaminant barrier
- It reduces component friction
- It decreases usage wear
- It stabilizes the bearing structure
There are 3 Types of bearing lubricants
1. Grease Lubricant
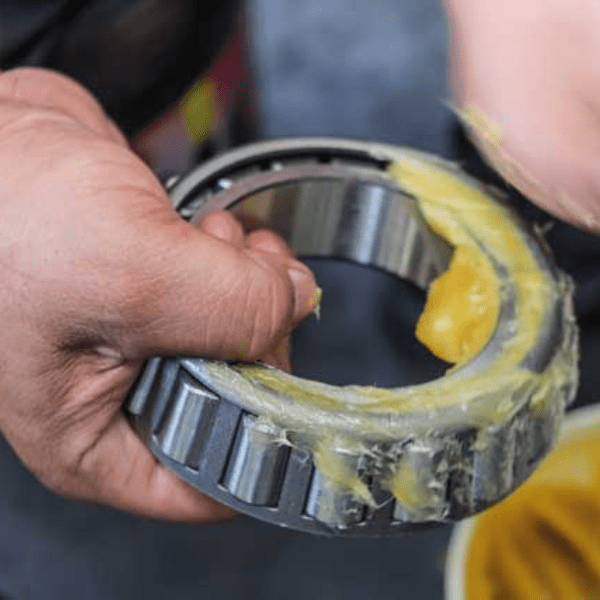

Grease lubricant is composed of oil base and thickener, which provides varying viscosity from fluid to semi-solid state. It offers versatility in applications for bearings and requires less frequent maintenance. However, due to its partial-solid composition, it may not be suitable for high-load speeds or improper mounting. Nonetheless, grease lubricant provides added protection against corrosion and oxidation.
2. Oil Lubricant
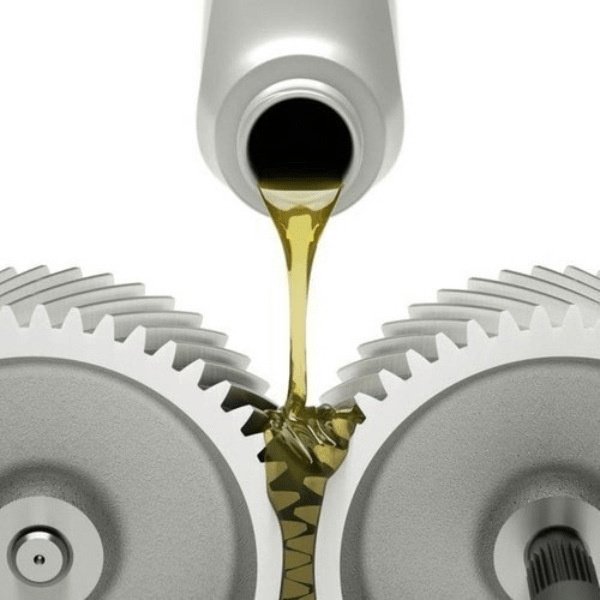

Compared to grease lubricants, synthetic or petroleum-based oils are capable of withstanding high load speeds and capacities, making them a suitable choice for mechanical operations that involve high production, and can prevent costly downtime. However, since oil is a highly fluid liquid that can evaporate when the bearing is not shielded, it needs regular maintenance, including various application methods such as jets and oil baths.
3. Solid Film Lubricant (Dry Lubricant)
3. Solid Film Lubricant (Dry Lubricant)

Solid film lubricants, such as graphite, boron nitride, molybdenum disulphide, or tungsten disulphide, can be applied onto bearings through burnishing or sputtering to create a solid film in the raceways and balls. Nonetheless, these lubricants are usually considered as a final option for extreme conditions such as vacuum-sealed or radioactive environments.
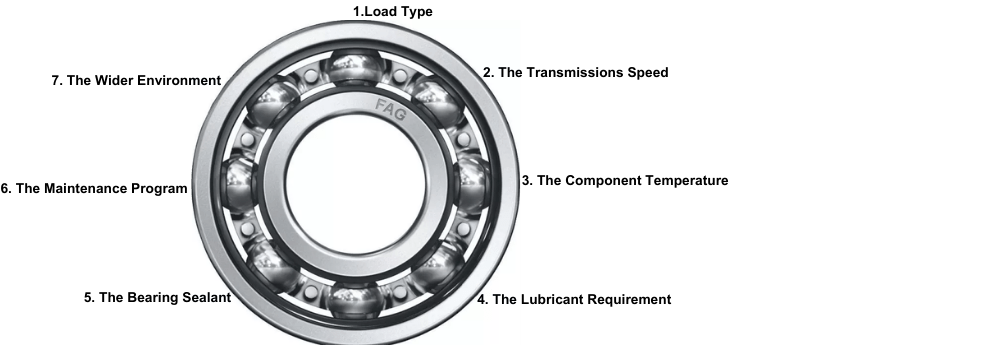
What things should we consider while selecting a Lubricant:
When choosing a lubricant for your mechanical operations and power transmission components, several factors should be taken into account.
The first is the operating temperature of the equipment, as high speeds and loads generate significant heat that the lubricant must be able to tolerate. If the bearing is not shielded, oil lubricant may evaporate, making grease a better choice if the external conditions and contaminants allow it.
The second factor to consider is the bearing speed and the type of lubrication needed to maintain the appropriate level of friction under those conditions. Grease is not suitable for high speeds, while both petroleum-based and synthetic oils provide the required protection for your bearings sourced from the bearing supplier of Singapore.
The third factor is the harshness of the operating conditions. In environments with high contamination, radioactivity, or vacuum, it’s essential to avoid downtime by selecting a lubricant that can withstand these conditions. In such cases, it may be necessary to apply a dry lubricant in the form of a solid film on the bearing components.
It’s also crucial to consider the viscosity of the lubricant at operational speeds and temperatures. Oils, greases, and dry lubricants can polymerize in transmission, resulting in uneven, tacky layers that act as “speed bumps,” reducing smooth movement and causing unnecessary downtime. Therefore, it’s vital to use lubricants that can withstand temperatures up to 148°C (300°F) when necessary.
3 Best Practices for Lubrication Application
Bearing lubrication is a consistent consideration when looking to improve mechanical operations and reduce downtime. That said, there are three best practices from prior installation to post-management for your bearing, no matter the industry or application.
1. Select the Correct Lubricant
The first essential practice is to carefully choose the appropriate precision component that can offer reliable and efficient frictionless power transmission for your device. This involves considering factors such as the lubrication type, the operating environment, the application, and the bearing type.
2. Apply the Lubricant Correctly
Once you have obtained the appropriate lubricant, it’s crucial to understand the application process and whether your chosen lubricant is suitable for your application requirements. Since some lubricants may require precision tools, you may need the assistance of full-service professionals like the SantEnt. In addition to supplying high-quality bearings, we also offer professional installation services.
3. Maintain the Lubricant Properly
Lastly, during production, your bearing may experience lubricant loss or contamination. Loss can happen due to bearing misalignment or oil evaporation, while contamination occurs when the lubricant comes into contact with surrounding environmental elements like dust or debris. With a well-planned preventive maintenance schedule, your lubrication can provide long-lasting protection for your bearing.
From where we should choose the Appropriate Bearing for Your Machinery
Santiniketan Enterprises, also known as SantEnt, has been in operation since 1977. We are known for Distributing high-quality Industrial products to customers in many countries across six continents. We deal in over 50 globally renowned brands which manufacture industrial spares and power transmission solutions like bearing, belts, maintenance products and related accessories
SantEnt is dedicated to providing top-quality products and service to its customers.